Parathyroid Disease (High Calcium)
 |
We are seeing an increasing number of patients who are having side effects from elevated blood calcium levels due to parathyroid disease. Commonly these patients initially present with kidney stones (often multiple episodes) or loss of bone density (osteoporosis).
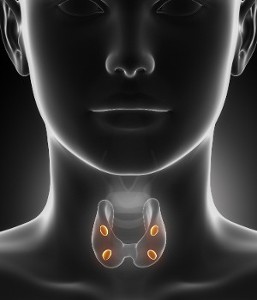
The parathyroid glands are four small glands surrounding the thyroid gland in the front of the neck just above the collar bones. These glands have no relationship to the thyroid gland itself, other than they are anatomic neighbors. The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone which increases blood calcium levels by pulling calcium out of the bones and reducing its loss in the urine. People may develop a benign growth (parathyroid adenoma) of one (or in a small fraction of patients, more than one) of the parathyroid glands causing an over-production of parathyroid hormone which elevates the blood calcium level. Elevated blood calcium levels may lead to kidney stones or osteoporosis, as well as more vague symptoms like bone/joint/abdominal pain or mood disorders like depression.
|
If a patient is shown to have elevated blood calcium he/she should have their parathyroid hormone level checked as well. Patients with elevated calcium who also have an elevated parathyroid hormone level are suspected to have a parathyroid adenoma. If the blood labs do not clarify completely, the patient may be asked to complete a 24-hour urine collection, where all of a patient’s urine is collected over a 24-hour period and the total amount of calcium is measured. If the calcium in a 24-hour urine collection is very high, this suggests hyperparathyroidism. Diagnostic imaging is often employed in an attempt to identify which gland has the adenoma. Imaging may be ultrasound, a nuclear scan called a Sestamibi scan, or a 4D CT scan. The treatment for parathyroid adenoma is typically surgery to remove the offending gland(s).